Mindfulness Made Simple – Techniques to Calm Your Busy Mind

Mindfulness: 5 Simple Techniques for Calm
Mindfulness: Cut Anxiety by 50% in 10 Minutes a Day—Start Now
Mindfulness is the practice of paying attention to the present moment without judgment—and it might be exactly what your overwhelmed brain needs. In our always-on world, we juggle endless tasks and notifications, which contributes to widespread anxiety.
Quick Answer: What is Mindfulness?
- Definition: Awareness of your thoughts, feelings, and surroundings in the present moment
- Purpose: Reduce stress, improve focus, and build emotional resilience
- Practice: Simple techniques like mindful breathing, body scans, and grounding exercises
- Time needed: Just 5-10 minutes daily can create measurable benefits
- Evidence: Proven to reduce anxiety by up to 50% and lower blood pressure
The good news? You don’t need hours of meditation. Research shows that even 10 minutes of daily mindfulness practice can significantly improve mental health. Studies from Harvard Medical School demonstrate that mindfulness literally rewires your brain, strengthening areas responsible for emotional regulation while calming the stress response.
Whether you’re dealing with racing thoughts or struggling to sleep, mindfulness offers practical tools that fit into any schedule. These techniques work anywhere, anytime.
As Anna Green, LMHC, LPC, and Chief Clinical Officer at Thrive Mental Health, I’ve seen how mindfulness transforms lives. It serves as a foundation for deeper healing and sustainable mental wellness.
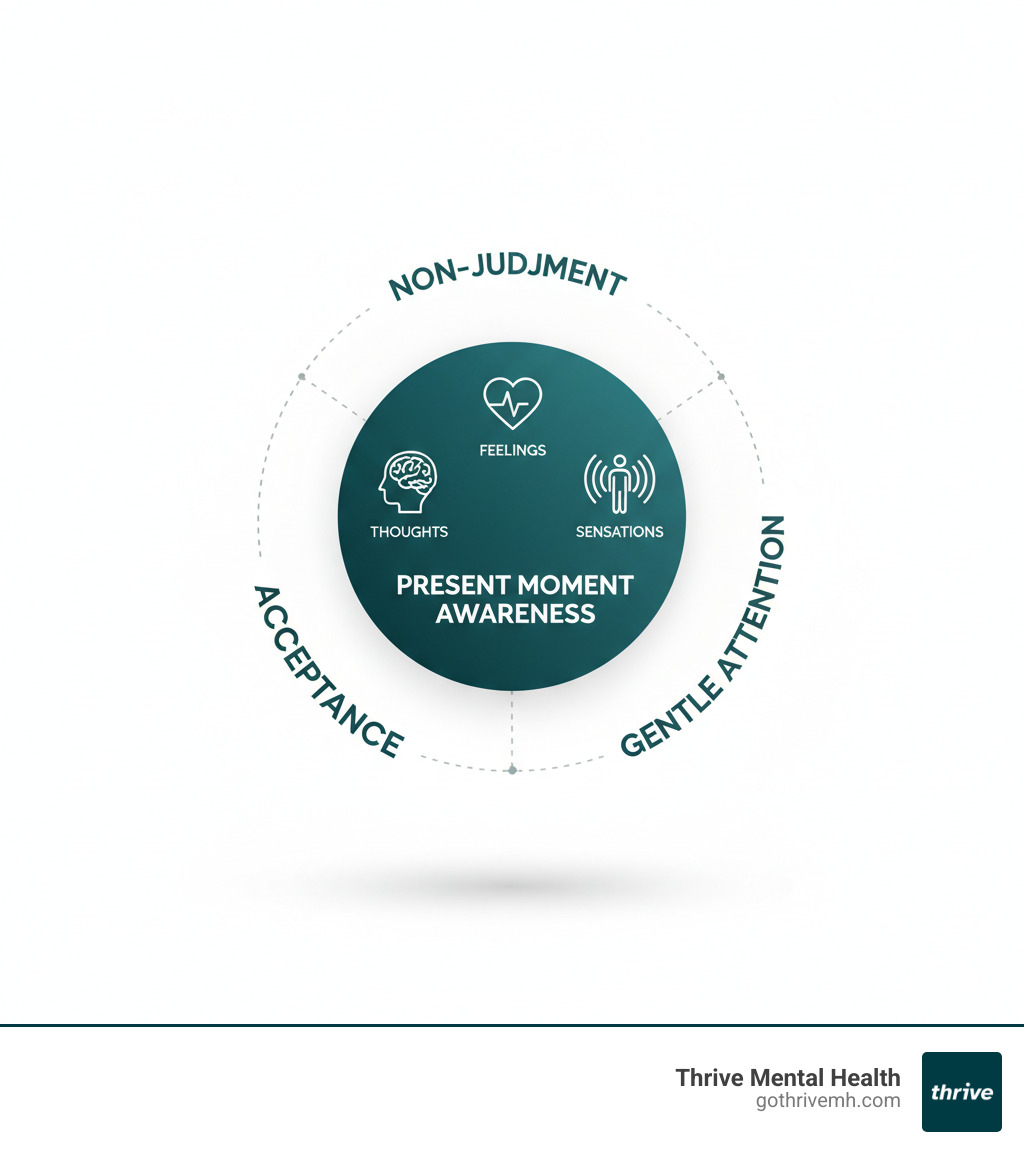
What Is Mindfulness? (And Why It Matters)
Imagine sitting by a river, watching leaves—representing your thoughts and feelings—drift by. Mindfulness is being that calm observer on the riverbank, noticing what passes without getting swept away or trying to control the current.
At its heart, mindfulness means paying attention to what’s happening right now, inside and around you, without judgment. The APA Dictionary of Psychology defines it as awareness of one’s internal states and surroundings. We learn to watch our thoughts and emotions like clouds passing overhead rather than getting caught in every mental storm.
Jon Kabat-Zinn, who brought mindfulness into mainstream healthcare, describes it as “paying attention on purpose, in the present moment, non-judgmentally.” It’s like hitting the pause button on life’s constant rush to simply notice what’s happening.
The core principles are attention and intention. We intentionally focus our attention on the present—the feeling of our breath, the warmth of sunlight, or the taste of coffee. This helps us see our thoughts and feelings as temporary visitors.
Acceptance also plays a huge role. Instead of fighting uncomfortable feelings, we treat ourselves with kindness. This gentle, non-reactive approach creates space for peace and clarity.
The Difference Between Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness and meditation are often confused. Mindfulness is a quality of mind we all have—that moment you’re fully absorbed in a simple task or completely present in a conversation.
Meditation, on the other hand, is the formal practice, like going to the gym for your mind. It involves dedicated minutes of sitting quietly, doing body scans, or walking with intention. These exercises train your mindfulness muscle, making it stronger and more accessible throughout your day.
| Feature | Mindfulness | Meditation |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Present-moment awareness and acceptance of what is | Training your mind to cultivate focus, calm, and insight |
| Practice | Can happen anytime, anywhere – washing dishes, walking, talking | Formal, dedicated practice sessions with specific techniques |
| Application | Woven throughout daily life to reduce stress and reactivity | Structured time that builds skills for everyday mindfulness |
They work together: formal meditation makes it easier to stay mindful during a stressful meeting, and mindful moments throughout your day deepen your meditation.
The Ancient Roots of a Modern Practice
Mindfulness isn’t a new trend; it has roots stretching back over 2,500 years in Buddhist tradition, where the Pali word “sati” meant “remembering” to be present.
Modern pioneers like Jon Kabat-Zinn adapted these ancient practices for our contemporary world. They stripped away religious elements while keeping the powerful core techniques, making mindfulness available to anyone, regardless of belief.
Today, mindfulness is recognized by institutions like the National Institutes of Health as an evidence-based approach for wellness. It taps into a universal human capacity for presence and awareness, offering practical tools for anyone dealing with the stresses of modern life.
The Science Is In: 7 Proven Benefits of a Mindful Practice
Rigorous scientific research now confirms what practitioners have known for centuries: mindfulness creates real, measurable changes in both mind and body. The scientific research on mindfulness for your health from the National Institutes of Health shows impressive results.
- Stress reduction: Studies document significant drops in psychological stress and physical stress markers like cortisol. It gives your overworked nervous system a chance to relax.
- Anxiety relief: Mindfulness trains your brain to observe anxious thoughts without getting hijacked by them. You learn to notice anxiety, acknowledge it, and let it pass.
- Depression management: Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) helps people develop a new relationship with their thoughts, learning to “de-center” from negative patterns. It’s about recognizing thoughts are just mental events, not facts.
- Improved focus and concentration: In our distraction-heavy world, mindfulness acts like strength training for your attention span, improving performance in work, academics, and even athletics.
- Deeper self-insight and compassion: By observing your internal world without judgment, you understand your patterns and needs with greater clarity. This self-awareness extends outward, fostering patience with others.
- Physical health benefits: Research shows mindfulness can lower blood pressure, boost immune function, and help manage chronic conditions.
- Healthier habits: As you become more aware of your body’s signals and emotional triggers, making conscious choices about things like food becomes easier.
How Mindfulness Rewires Your Brain for Happiness
Your brain’s neuroplasticity means that mindfulness practice literally reshapes its structure.
Brain scans show reduced amygdala activity in meditators. The amygdala is the brain’s alarm system; mindfulness calms this hypervigilance, creating a more peaceful state. Simultaneously, there is increased prefrontal cortex density in areas responsible for attention and emotional regulation. This strengthens your brain’s “CEO,” allowing for thoughtful responses rather than impulsive reactions.
This remodeling explains why emotional regulation improves so dramatically. You learn to feel emotions without being overwhelmed by them. The de-centering effect is particularly powerful for depression, with MBCT showing reduced relapse rates of 50% for those with a history of depressive episodes. Even improved pain management is evident, as meditation can reduce pain intensity by changing how the brain processes pain signals.
Better Sleep, Less Pain, and a Healthier Body
The effects of mindfulness extend throughout your physical health.
- Lower blood pressure is a consistent finding, as the cardiovascular system responds to reduced stress.
- Improved sleep quality is often one of the first benefits people notice. A quieter mind makes it easier to fall asleep.
- For chronic pain coping, mindfulness helps change your relationship with the pain. While the sensation may remain, the suffering around it often dissolves.
- Immune system support gets a boost. By reducing chronic stress, which suppresses immunity, mindfulness helps restore the body’s natural defenses.
- Healthier eating habits often develop naturally. Mindful eating helps you notice hunger and fullness cues, which can lead to reduced binge eating without restrictive diets.
5 Simple Mindfulness Techniques You Can Start Today
Starting a mindfulness practice is simple. We believe in starting small, making consistency your goal. Even a few minutes a day can create noticeable shifts. These techniques require no special equipment—just your willingness to be present.

1. Mindful Breathing
This fundamental technique uses your breath as an anchor to the present moment.
How to Practice:
- Find a comfortable position and gently close your eyes.
- Bring your attention to your breath. Notice the sensation of air entering and leaving your body.
- Feel the rise and fall of your chest or abdomen.
- When your mind wanders (which is normal!), gently guide your attention back to your breath without judgment.
- Start with 1-3 minutes.
2. The Body Scan
This is a powerful way to cultivate body awareness and release hidden tension.
How to Practice:
- Lie down or sit in a relaxed position with your eyes closed.
- Bring your attention to your toes, noticing any sensations (tingling, warmth, pressure) without judgment.
- Slowly move your attention up through your body: feet, legs, torso, arms, neck, and head.
- As you scan each area, simply notice what’s present. If you find tension, imagine your breath softening and releasing it.
- Gently guide your mind back to the body part if it wanders.
3. Mindful Walking
Turn a daily activity into an informal mindfulness practice.
How to Practice:
- As you walk, bring your attention to the sensation of your feet on the ground.
- Pay attention to the movement of your body and the rhythm of your pace.
- Notice the sounds and sights around you without labeling them as good or bad.
- If your mind starts planning or worrying, gently bring your focus back to the physical act of walking.
4. The 5-4-3-2-1 Grounding Technique
This technique uses your senses to quickly pull you back to the present when you feel anxious or overwhelmed.
How to Practice:
- Take a deep breath.
- 5: See – Name five things you can see.
- 4: Feel – Identify four things you can feel (e.g., your clothes, the chair).
- 3: Hear – Listen for three distinct sounds.
- 2: Smell – Notice two things you can smell.
- 1: Taste – Identify one thing you can taste.

5. Mindful Observation (The Raisin Exercise)
This exercise cultivates curiosity and appreciation for simple experiences. It can be done with any small object or piece of food.
How to Practice:
- See: Look at the object closely, noticing its color, shape, and texture.
- Touch: Feel its texture and weight.
- Smell: Inhale any scent it has.
- Taste/Experience: If it’s food, place it in your mouth without chewing. Notice how it feels. Then, slowly chew, noticing the flavor and texture changes. Finally, notice the sensation of swallowing.
If you find yourself struggling with persistent stress or anxiety, professional support can make a significant difference. Explore how online therapy for stress can provide custom guidance and additional techniques.
Integrating Mindfulness into Your Life and Professional Therapy
The real power of mindfulness unfolds when you weave it into the ordinary moments of your day.
- Mindful eating: Instead of scrolling on your phone during lunch, truly taste your food. Notice the flavors and textures. This can transform your relationship with food.
- Mindful commuting: Turn a frustrating commute into a moment of calm. Notice the colors of the sky or feel your hands on the steering wheel to arrive more centered.
- Single-tasking: Pick one task and give it your full attention. When your mind wanders, gently guide it back. You’ll feel more effective and less stressed.
- Mindful listening: When someone is talking, truly hear them instead of planning your reply. This deepens every interaction.
- Digital detox moments: Put your phone away during dinner or take a walk without earbuds. These breaks help you reconnect with yourself and the world.
Mindfulness in Modern Therapy: MBSR and MBCT
The integration of mindfulness into professional therapy has created some of today’s most effective, evidence-based treatments for anxiety, depression, and stress.
- Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR): This 8-week program combines meditation and body scans to help people manage everything from chronic pain to overwhelming stress. You learn to observe your thoughts and feelings without getting swept away by them.
- Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT): This approach adds cognitive behavioral techniques to prevent depression relapse. It teaches you to recognize early warning signs and respond differently, seeing thoughts as passing mental events. Studies show it can cut depression relapse rates in half.
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT): ACT uses mindfulness to help you accept difficult thoughts and feelings while still moving toward what matters most to you, building psychological flexibility.
These approaches work by offering a third option beyond fighting or getting lost in difficult experiences: acknowledgment without attachment. Our Intensive Outpatient Program (IOP) incorporates these evidence-based mindfulness techniques into comprehensive care.
Finding Mindfulness-Based Care in Florida
Finding quality mindfulness-based care is accessible throughout Florida. Whether you’re in Miami dealing with work stress or in Orlando managing anxiety, Thrive Mental Health brings evidence-based programs to you through virtual and hybrid options.
Our Intensive Outpatient Programs (IOP) and Partial Hospitalization Programs (PHP) integrate mindfulness with other therapeutic approaches. Prefer 1:1 support? Explore our Virtual Therapy options for Florida.
Our virtual platform allows you to access expert-led care from your home in Jacksonville or your office in Tampa.
We know navigating insurance can be a barrier, which is why we work with major plans including Cigna, Optum, and Florida Blue. You can verify your insurance coverage in minutes with no obligation. We also offer evening sessions because mental health care should fit into your life. Our goal is to help you build a sustainable practice that supports your mental health long-term.
For a quick primer you can use today, read our related blog: 7 Mindfulness Exercises You Can Do in 5 Minutes.
Frequently Asked Questions about Mindfulness
Starting something new can bring up questions. Here are the honest answers to what we hear most often about mindfulness.
How do I start a daily mindfulness practice?
Starting is simple. You don’t need special equipment or hours of free time. Start with just 5 minutes a day. Anchor the practice to an existing routine, like while your morning coffee brews.
Guided meditations on apps or websites are a great way to begin. Most importantly, be patient with yourself. Your mind will wander—that’s normal. Each time you gently guide your focus back, you’re strengthening your mindfulness muscle. There is no “right” way to do it.
Can mindfulness be harmful or make anxiety worse?
For most people, mindfulness is a safe and gentle practice. However, in rare cases and without proper guidance, it can surface difficult emotions or memories, which may feel overwhelming for those with a history of trauma or severe anxiety.
The key is learning from qualified sources. If you have a history of severe mental health conditions or find that mindfulness increases your distress, working with a trained therapist is crucial. At Thrive, our clinicians are trained to adapt these practices to your specific needs, ensuring a safe and supportive approach.
How long does it take for mindfulness to work?
Some benefits, like feeling calmer, can happen almost immediately after a short session.
However, lasting changes for anxiety, depression, or chronic stress typically develop over several weeks of consistent practice. Research on 8-week MBSR courses shows profound shifts in how the brain responds to stress. Think of it like fitness: you feel good after one workout, but real change comes from consistent effort over time. Most people notice meaningful improvements around the 3-4 week mark.
Does insurance cover mindfulness-based therapy (MBSR/MBCT)?
Often, yes—especially when delivered as part of evidence-based care like IOP/PHP or individual therapy. We work with major plans including Cigna, Optum, and Florida Blue in Florida. Check your benefits here → Verify insurance.
What if I can’t sit still—can I still practice mindfulness?
Yes. Try movement-based options like mindful walking, yoga, or brief (1–3 minute) breathing exercises. Many people with busy minds or ADHD find these more approachable.
FAQ Schema (JSON-LD suggestion)
Ready for support? Thrive offers virtual and hybrid IOP/PHP with evening options. Verify your insurance in 2 minutes (no obligation) → Start benefits check or call 561-203-6085. If you’re in crisis, call/text 988.